迭代图处理
Gelly利用Flink的高效迭代 算子来支持大规模迭代图处理。目前,我们提供了以顶点为中心,分散 - 聚集和聚合 - 求 - 应用模型的实现。在以下部分中,我们将介绍这些抽象,并展示如何在Gelly中使用它们。
以顶点为中心的迭代
以顶点为中心的模型,也称为“像顶点一样思考”或“Pregel”,从图中顶点的角度表示计算。计算在同步迭代步骤中进行,称为超级步骤。在每个超级步骤中,每个顶点执行一个用户定义的函数。顶点通过消息与其他顶点通信。顶点可以向图中的任何其他顶点发送消息,只要它知道其唯一ID即可。
计算模型如下图所示。虚线框对应于并行化单元。在每个超级步骤中,所有活动顶点并行执行相同的用户定义计算。超级步骤是同步执行的,因此保证在一个超级步骤期间发送的消息在下一个超级步骤的开始时传递。
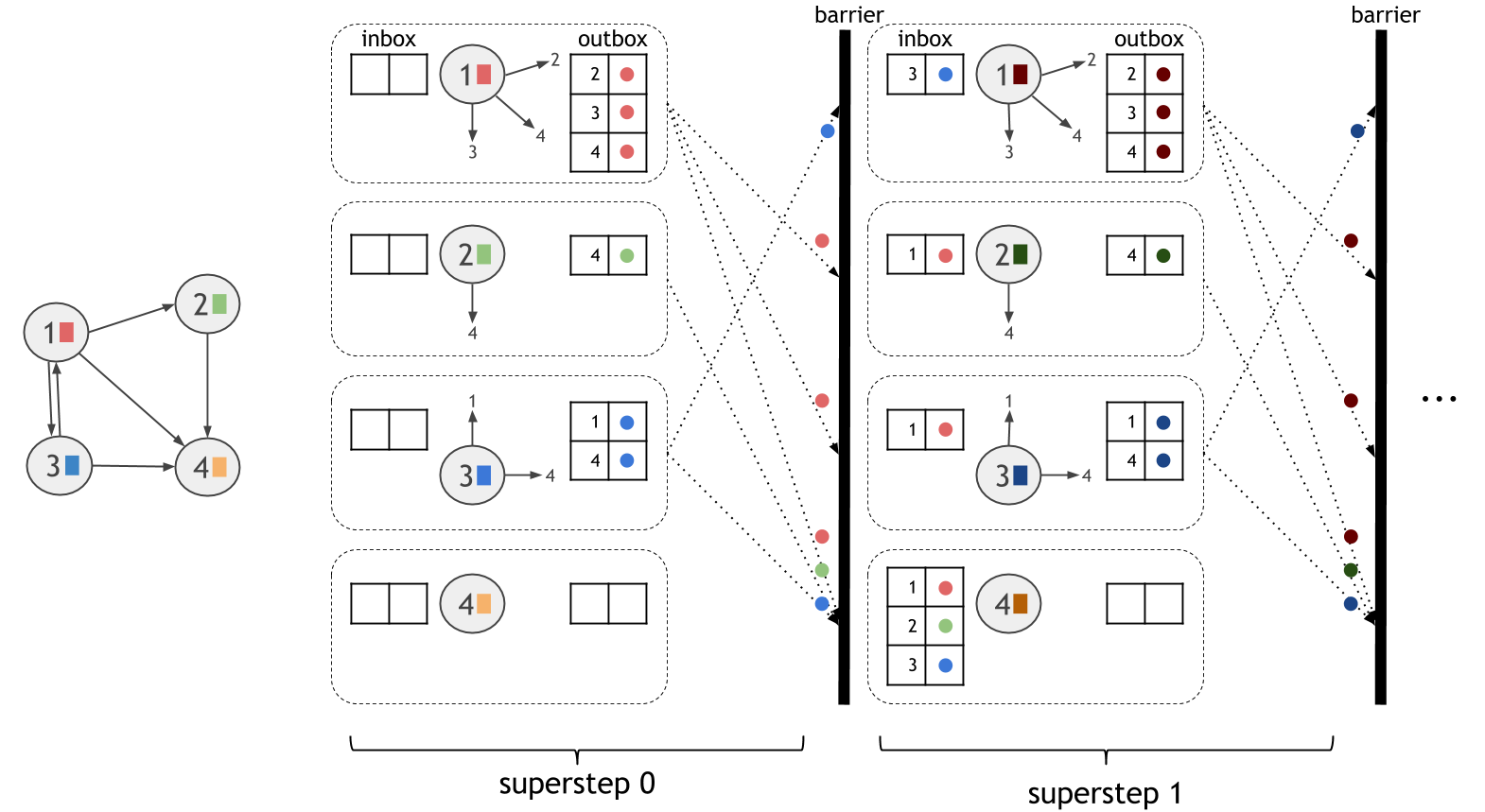
要在Gelly中使用以顶点为中心的迭代,用户只需要定义顶点计算函数,ComputeFunction。该函数和最大运行迭代次数作为Gelly的参数给出runVertexCentricIteration。此方法将在输入Graph上执行以顶点为中心的迭代,并返回具有更新顶点值的新Graph。MessageCombiner可以定义可选的消息组合器以降低通信成本。
让我们考虑使用以顶点为中心的迭代来计算单源最短路径。最初,每个顶点都具有无限距离的值,除了源顶点,其值为零。在第一个超级步骤期间,源将距离传播到其邻居。在以下超级步骤中,每个顶点检查其接收的消息并选择它们之间的最小距离。如果此距离小于其当前值,则更新其状态并为其邻居生成消息。如果顶点在超级步骤期间没有改变其值,则它不会为其下一个超级步的邻居生成任何消息。当没有值更新或达到最大超级步数时,算法收敛。在这个算法中,
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the vertex-centric iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(
new SSSPComputeFunction(), new SSSPCombiner(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
public static final class SSSPComputeFunction extends ComputeFunction<Long, Double, Double, Double> {
public void compute(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex, MessageIterator<Double> messages) {
double minDistance = (vertex.getId().equals(srcId)) ? 0d : Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (Double msg : messages) {
minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, msg);
}
if (minDistance < vertex.getValue()) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance);
for (Edge<Long, Double> e: getEdges()) {
sendMessageTo(e.getTarget(), minDistance + e.getValue());
}
}
}
// message combiner
public static final class SSSPCombiner extends MessageCombiner<Long, Double> {
public void combineMessages(MessageIterator<Double> messages) {
double minMessage = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (Double msg: messages) {
minMessage = Math.min(minMessage, msg);
}
sendCombinedMessage(minMessage);
}
}
// read the input graph val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the vertex-centric iteration val result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(new SSSPComputeFunction, new SSSPCombiner, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
final class SSSPComputeFunction extends ComputeFunction[Long, Double, Double, Double] {
override def compute(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double], messages: MessageIterator[Double]) = {
var minDistance = if (vertex.getId.equals(srcId)) 0 else Double.MaxValue
while (messages.hasNext) {
val msg = messages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
if (vertex.getValue > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance)
for (edge: Edge[Long, Double] <- getEdges) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget, vertex.getValue + edge.getValue)
}
}
}
// message combiner final class SSSPCombiner extends MessageCombiner[Long, Double] {
override def combineMessages(messages: MessageIterator[Double]) {
var minDistance = Double.MaxValue
while (messages.hasNext) {
val msg = inMessages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
sendCombinedMessage(minMessage)
}
}
配置以顶点为中心的迭代
可以使用VertexCentricConfiguration对象配置以顶点为中心的迭代。目前,可以指定以下参数:
-
名称:以顶点为中心的迭代的名称。名称显示在日志和消息中,可以使用该
setName()方法指定。 -
并行性:迭代的并行性。可以使用该
setParallelism()方法进行设置。 -
在非托管内存中设置的解决方案:定义解决方案集是保存在托管内存中(Flink的内部方式是以序列化形式保存对象)还是作为简单的对象映射。默认情况下,解决方案集在托管内存中运行。可以使用该
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法设置此属性。 -
聚合器:可以使用该
registerAggregator()方法注册迭代聚合器。迭代聚合器按超级步骤全局组合所有聚合,并使它们在下一个超级步骤中可用。可以在用户定义的内部访问已注册的聚合器ComputeFunction。 -
广播变量:数据集可以作为广播变量的
ComputeFunction使用,addBroadcastSet()方法。 - Scala
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
VertexCentricConfiguration parameters = new VertexCentricConfiguration();
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration");
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16);
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator());
// run the vertex-centric iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Long, Double> result =
graph.runVertexCentricIteration(
new Compute(), null, maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined function
public static final class Compute extends ComputeFunction {
LongSumAggregator aggregator = new LongSumAggregator();
public void preSuperstep() {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator");
}
public void compute(Vertex<Long, Long> vertex, MessageIterator inMessages) {
//do some computation
Long partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue);
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...);
}
}
val graph: Graph[Long, Long, Double] = ...
val parameters = new VertexCentricConfiguration
// set the iteration name parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration")
// set the parallelism parameters.setParallelism(16)
// register an aggregator parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator)
// run the vertex-centric iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runVertexCentricIteration(new Compute, new Combiner, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined function final class Compute extends ComputeFunction {
var aggregator = new LongSumAggregator
override def preSuperstep {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator")
}
override def compute(vertex: Vertex[Long, Long], inMessages: MessageIterator[Long]) {
//do some computation
val partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue)
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...)
}
}
分散 - 收集迭代
分散 - 聚集模型,也称为“信号/收集”模型,从图中的顶点的角度表示计算。计算在同步迭代步骤中进行,称为超级步骤。在每个超级步骤中,顶点为其他顶点生成消息,并根据它接收的消息更新其值。要在Gelly中使用分散 - 聚集迭代,用户只需要定义顶点在每个超级步骤中的行为:
- Scatter:生成顶点将发送到其他顶点的消息。
- 收集:使用收到的消息更新顶点值。
Gelly提供了分散 - 聚集迭代的方法。用户只需要实现两个函数,对应于分散和聚集阶段。第一个函数是a ScatterFunction,它允许顶点将消息发送到其他顶点。在发送消息的过程中收到消息。第二个函数是GatherFunction,它定义了顶点如何根据接收的消息更新其值。这些函数和运行的最大迭代次数作为Gelly的参数给出runScatterGatherIteration。此方法将对输入Graph执行分散 - 聚集迭代,并返回具有更新顶点值的新Graph。
可以使用诸如顶点总数,入度和出度等信息来扩展分散 - 聚集迭代。另外,可以指定运行分散 - 聚集迭代的邻域类型(输入/输出/全部)。默认情况下,来自邻居的更新用于修改当前顶点的状态,并将消息发送到邻居。
让我们考虑在下图中使用散射 - 聚集迭代计算单源最短路径,并让顶点1成为源。在每个超级步骤中,每个顶点向其所有邻居发送候选距离消息。消息值是顶点的当前值与连接此顶点与其邻居的边缘权重之和。在接收候选距离消息时,每个顶点计算最小距离,并且如果已发现较短路径,则其更新其值。如果顶点在超级步骤期间没有改变其值,则它不会为其下一个超级步的邻居生成消息。当没有值更新时,算法收敛。
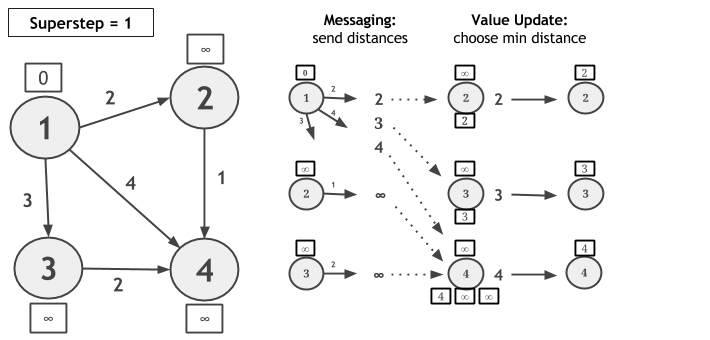
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the scatter-gather iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new MinDistanceMessenger(), new VertexDistanceUpdater(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// scatter: messaging
public static final class MinDistanceMessenger extends ScatterFunction<Long, Double, Double, Double> {
public void sendMessages(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex) {
for (Edge<Long, Double> edge : getEdges()) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget(), vertex.getValue() + edge.getValue());
}
}
}
// gather: vertex update
public static final class VertexDistanceUpdater extends GatherFunction<Long, Double, Double> {
public void updateVertex(Vertex<Long, Double> vertex, MessageIterator<Double> inMessages) {
Double minDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (double msg : inMessages) {
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg;
}
}
if (vertex.getValue() > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance);
}
}
}
// read the input graph val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the scatter-gather iteration val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new MinDistanceMessenger, new VertexDistanceUpdater, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// messaging final class MinDistanceMessenger extends ScatterFunction[Long, Double, Double, Double] {
override def sendMessages(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double]) = {
for (edge: Edge[Long, Double] <- getEdges) {
sendMessageTo(edge.getTarget, vertex.getValue + edge.getValue)
}
}
}
// vertex update final class VertexDistanceUpdater extends GatherFunction[Long, Double, Double] {
override def updateVertex(vertex: Vertex[Long, Double], inMessages: MessageIterator[Double]) = {
var minDistance = Double.MaxValue
while (inMessages.hasNext) {
val msg = inMessages.next
if (msg < minDistance) {
minDistance = msg
}
}
if (vertex.getValue > minDistance) {
setNewVertexValue(minDistance)
}
}
}
配置Scatter-Gather迭代
可以使用ScatterGatherConfiguration对象配置分散 - 聚集迭代。目前,可以指定以下参数:
-
名称:分散 - 聚集迭代的名称。名称显示在日志和消息中,可以使用该
setName()方法指定。 -
并行性:迭代的并行性。可以使用该
setParallelism()方法进行设置。 -
在非托管内存中设置的解决方案:定义解决方案集是保存在托管内存中(Flink的内部方式是以序列化形式保存对象)还是作为简单的对象映射。默认情况下,解决方案集在托管内存中运行。可以使用该
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法设置此属性。 -
聚合器:可以使用该
registerAggregator()方法注册迭代聚合器。迭代聚合器按超级步骤全局组合所有聚合,并使它们在下一个超级步骤中可用。注册可聚合内的用户定义的访问ScatterFunction和GatherFunction。 -
广播变量:DataSet可以分别作为广播变量添加到
ScatterFunction和GatherFunction使用addBroadcastSetForUpdateFunction()和addBroadcastSetForMessagingFunction()方法。 -
顶点数:访问迭代中顶点的总数。可以使用该
setOptNumVertices()方法设置此属性。然后可以使用该getNumberOfVertices()方法在顶点更新函数和消息传递函数中访问顶点的数量。如果未在配置中设置该选项,则此方法将返回-1。 -
度:访问迭代中顶点的输入/输出度。可以使用该
setOptDegrees()方法设置此属性。然后可以使用getInDegree()和getOutDegree()方法在顶点更新函数和消息传递函数中访问每个顶点的输入/输出度。如果未在配置中设置degrees选项,则这些方法将返回-1。 -
消息传递方向:默认情况下,顶点会向其邻居发送消息,并根据从其邻居收到的消息更新其值。此配置选项允许用户将消息传送方向改变为任一
EdgeDirection.IN,EdgeDirection.OUT,EdgeDirection.ALL。消息传递方向也决定这将是更新方向EdgeDirection.OUT,EdgeDirection.IN和EdgeDirection.ALL分别。可以使用该setDirection()方法设置此属性。 - Scala
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the iteration name
parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration");
// set the parallelism
parameters.setParallelism(16);
// register an aggregator
parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator());
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
LongSumAggregator aggregator = new LongSumAggregator();
public void preSuperstep() {
// retrieve the Aggregator
aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator");
}
public void updateVertex(Vertex<Long, Long> vertex, MessageIterator inMessages) {
//do some computation
Long partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value
aggregator.aggregate(partialValue);
// update the vertex value
setNewVertexValue(...);
}
}
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the iteration name parameters.setName("Gelly Iteration")
// set the parallelism parameters.setParallelism(16)
// register an aggregator parameters.registerAggregator("sumAggregator", new LongSumAggregator)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
var aggregator = new LongSumAggregator
override def preSuperstep {
// retrieve the Aggregator aggregator = getIterationAggregator("sumAggregator")
}
override def updateVertex(vertex: Vertex[Long, Long], inMessages: MessageIterator[Long]) {
//do some computation val partialValue = ...
// aggregate the partial value aggregator.aggregate(partialValue)
// update the vertex value setNewVertexValue(...)
}
}
以下示例说明了度数的使用以及顶点选项的数量。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true);
// set the degree option to true
parameters.setOptDegrees(true);
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {
...
// retrieve the vertex out-degree
outDegree = getOutDegree();
...
}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// configure the iteration val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the number of vertices option to true parameters.setOptNumVertices(true)
// set the degree option to true parameters.setOptDegrees(true)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {
...
// retrieve the vertex out-degree val outDegree = getOutDegree
...
}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {
...
// get the number of vertices val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
以下示例说明了边缘方向选项的用法。顶点更新其值以包含其所有邻居的列表。
Graph<Long, HashSet<Long>, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
ScatterGatherConfiguration parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration();
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN);
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
DataSet<Vertex<Long, HashSet<Long>>> result =
graph.runScatterGatherIteration(
new Messenger(), new VertexUpdater(), maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices();
// user-defined functions
public static final class Messenger extends GatherFunction {...}
public static final class VertexUpdater extends ScatterFunction {...}
val graph: Graph[Long, HashSet[Long], Double] = ...
// configure the iteration val parameters = new ScatterGatherConfiguration
// set the messaging direction parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN)
// run the scatter-gather iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runScatterGatherIteration(new Messenger, new VertexUpdater, maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices
// user-defined functions final class Messenger extends ScatterFunction {...}
final class VertexUpdater extends GatherFunction {...}
收集 - 应用迭代
与分散 - 聚集模型一样,Gather-Sum-Apply也在同步迭代步骤中进行,称为超级步骤。每个超级步骤包括以下三个阶段:
- 收集:在每个顶点的边和邻居上并行调用用户定义的函数,从而生成部分值。
- 总和:使用用户定义的reducer将聚集阶段中生成的部分值聚合为单个值。
- 应用:通过对当前值和Sum阶段生成的聚合值应用函数来更新每个顶点值。
让我们考虑在下图中用GSA计算单源最短路径,并让顶点1成为源。在该Gather阶段期间,我们通过将每个顶点值与边缘权重相加来计算新的候选距离。在Sum,候选距离按顶点ID分组,并选择最小距离。在Apply,将新计算的距离与当前顶点值进行比较,并将两者中的最小值指定为顶点的新值。
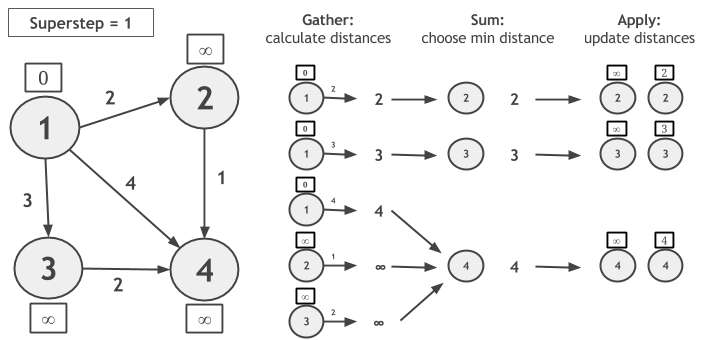
请注意,如果顶点在超级步骤期间未更改其值,则在下一个超级步骤期间不会计算候选距离。当没有顶点改变值时,算法收敛。
为了实现在冻膜GSA该示例中,用户只需要调用runGatherSumApplyIteration对输入图形的方法和提供的GatherFunction,SumFunction和ApplyFunctionUDF的。迭代同步,分组,值更新和收敛由系统处理:
// read the input graph
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations
int maxIterations = 10;
// Execute the GSA iteration
Graph<Long, Double, Double> result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new CalculateDistances(), new ChooseMinDistance(), new UpdateDistance(), maxIterations);
// Extract the vertices as the result
DataSet<Vertex<Long, Double>> singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices();
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// Gather
private static final class CalculateDistances extends GatherFunction<Double, Double, Double> {
public Double gather(Neighbor<Double, Double> neighbor) {
return neighbor.getNeighborValue() + neighbor.getEdgeValue();
}
}
// Sum
private static final class ChooseMinDistance extends SumFunction<Double, Double, Double> {
public Double sum(Double newValue, Double currentValue) {
return Math.min(newValue, currentValue);
}
}
// Apply
private static final class UpdateDistance extends ApplyFunction<Long, Double, Double> {
public void apply(Double newDistance, Double oldDistance) {
if (newDistance < oldDistance) {
setResult(newDistance);
}
}
}
// read the input graph val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// define the maximum number of iterations val maxIterations = 10
// Execute the GSA iteration val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new CalculateDistances, new ChooseMinDistance, new UpdateDistance, maxIterations)
// Extract the vertices as the result val singleSourceShortestPaths = result.getVertices
// - - - UDFs - - - //
// Gather final class CalculateDistances extends GatherFunction[Double, Double, Double] {
override def gather(neighbor: Neighbor[Double, Double]): Double = {
neighbor.getNeighborValue + neighbor.getEdgeValue
}
}
// Sum final class ChooseMinDistance extends SumFunction[Double, Double, Double] {
override def sum(newValue: Double, currentValue: Double): Double = {
Math.min(newValue, currentValue)
}
}
// Apply final class UpdateDistance extends ApplyFunction[Long, Double, Double] {
override def apply(newDistance: Double, oldDistance: Double) = {
if (newDistance < oldDistance) {
setResult(newDistance)
}
}
}
请注意,gather将Neighbor类型作为参数。这是一种便利类型,它简单地用相邻边包裹顶点。
有关如何使用Gather-Sum-Apply模型实现算法的更多示例,请检查Gelly的GSAPageRank和GSAConnectedComponents库方法。
配置Gather-Sum-Apply迭代
可以使用GSAConfiguration对象配置GSA迭代。目前,可以指定以下参数:
-
名称:GSA迭代的名称。名称显示在日志和消息中,可以使用该
setName()方法指定。 -
并行性:迭代的并行性。可以使用该
setParallelism()方法进行设置。 -
在非托管内存中设置的解决方案:定义解决方案集是保存在托管内存中(Flink的内部方式是以序列化形式保存对象)还是作为简单的对象映射。默认情况下,解决方案集在托管内存中运行。可以使用该
setSolutionSetUnmanagedMemory()方法设置此属性。 -
聚合器:可以使用该
registerAggregator()方法注册迭代聚合器。迭代聚合器按超级步骤全局组合所有聚合,并使它们在下一个超级步骤中可用。可以在用户定义的内部访问已注册的聚合器GatherFunction,SumFunction以及ApplyFunction。 -
广播变量:数据集可以作为广播变量的
GatherFunction,SumFunction并且ApplyFunction,使用该方法addBroadcastSetForGatherFunction(),addBroadcastSetForSumFunction()并addBroadcastSetForApplyFunction分别方法。 -
顶点数:访问迭代中顶点的总数。可以使用该
setOptNumVertices()方法设置此属性。然后可以使用该getNumberOfVertices()方法在聚集,求和和/或应用函数中访问顶点的数量。如果未在配置中设置该选项,则此方法将返回-1。 -
邻居方向:默认情况下,从顶点的邻居收集值。这可以使用该
setDirection()方法进行修改。
以下示例说明了顶点数选项的用法。
Graph<Long, Double, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
GSAConfiguration parameters = new GSAConfiguration();
// set the number of vertices option to true
parameters.setOptNumVertices(true);
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
Graph<Long, Long, Long> result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new Gather(), new Sum(), new Apply(),
maxIterations, parameters);
// user-defined functions
public static final class Gather {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
public static final class Sum {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
public static final class Apply {
...
// get the number of vertices
long numVertices = getNumberOfVertices();
...
}
val graph: Graph[Long, Double, Double] = ...
// configure the iteration val parameters = new GSAConfiguration
// set the number of vertices option to true parameters.setOptNumVertices(true)
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new Gather, new Sum, new Apply, maxIterations, parameters)
// user-defined functions final class Gather {
...
// get the number of vertices val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
final class Sum {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
final class Apply {
...
// get the number of vertices
val numVertices = getNumberOfVertices
...
}
以下示例说明了边缘方向选项的用法。
Graph<Long, HashSet<Long>, Double> graph = ...
// configure the iteration
GSAConfiguration parameters = new GSAConfiguration();
// set the messaging direction
parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN);
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters
DataSet<Vertex<Long, HashSet<Long>>> result =
graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(
new Gather(), new Sum(), new Apply(), maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices();
val graph: Graph[Long, HashSet[Long], Double] = ...
// configure the iteration val parameters = new GSAConfiguration
// set the messaging direction parameters.setDirection(EdgeDirection.IN)
// run the gather-sum-apply iteration, also passing the configuration parameters val result = graph.runGatherSumApplyIteration(new Gather, new Sum, new Apply, maxIterations, parameters)
.getVertices()
迭代抽象比较
尽管Gelly中的三个迭代抽象看起来非常相似,但了解它们之间的差异可以带来更高性能和可维护的程序。在这三者中,以顶点为中心的模型是最通用的模型,并且支持每个顶点的任意计算和消息传递。在分散 - 聚集模型中,生成消息的逻辑与更新顶点值的逻辑分离。因此,使用分散 - 聚集编写的程序有时更容易遵循和维护。将消息传递阶段与顶点值更新逻辑分开不仅使一些程序更容易遵循,而且还可能对性能产生积极影响。分散 - 收集实现通常具有较低的内存要求,因为不需要对收件箱(接收的消息)和发件箱(要发送的消息)数据结构的并发访问。然而,这种特性也限制了表现力并使一些计算模式不直观。当然,如果算法需要顶点同时访问其收件箱和发件箱,那么此算法在分散 - 聚集中的表达可能会有问题。强连通分量和近似最大权重匹配是这种图算法的示例。这种限制的直接后果是顶点不能生成消息并在同一阶段更新它们的状态。因此,决定是否基于其内容传播消息将需要将其存储在顶点值中,以便在随后的迭代步骤中聚集阶段可以访问它。类似地,如果顶点更新逻辑包括对相邻边缘的值的计算,这些必须包含在从分散到聚集阶段的特殊消息中。此类变通方法通常会导致更高的内存要求和非优雅,难以理解的算法实现。
Gather-sum-apply迭代也与分散 - 聚集迭代非常相似。实际上,任何可以表示为GSA迭代的算法也可以在分散 - 聚集模型中编写。分散 - 聚集模型的消息传递阶段等同于GSA的聚集和求和步骤:聚集可以被视为消息生成的阶段,而Sum是它们被路由到目标顶点的阶段。同样,值更新阶段对应于“应用”步骤。
两种实现之间的主要区别在于GSA的Gather阶段在边缘上并行计算,而消息传递阶段在顶点上分配计算。使用上面的SSSP示例,我们看到在散射 - 聚集情况的第一个超级步骤中,顶点1,2和3并行生成消息。顶点1生成3条消息,而顶点2和3分别生成一条消息。另一方面,在GSA情况下,计算在边缘上并行化:顶点1的三个候选距离值是并行产生的。因此,如果Gather步骤包含“重”计算,那么使用GSA并展开计算可能是更好的主意,而不是加重单个顶点。
这两个实现之间的另一个区别是分散 - 聚集实现在coGroup内部使用 算子,而GSA使用a reduce。因此,如果组合邻居值(消息)的函数需要整组计算值,则应使用scatter-gather。如果更新函数是关联的和可交换的,那么GSA的reducer可以提供更高效的实现,因为它可以使用组合器。
需要注意的另一件事是GSA严格地用于邻域,而在顶点中心和散射 - 聚集模型中,顶点可以向任何顶点发送消息,只要它知道它的顶点ID,无论它是否是邻居。最后,在Gelly的分散 - 聚集实现中,可以选择消息传递方向,即更新传播的方向。GSA尚不支持这一点,因此每个顶点将仅根据其邻居的值进行更新。
Gelly迭代模型之间的主要差异如下表所示。
| 迭代模型 | 更新函数 | 更新逻辑 | 沟通范围 | 通信逻辑 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顶点为中心 | 随意 | 随意 | 任何顶点 | 随意 |
| 分散 - 集中 | 随意 | 根据收到的消息 | 任何顶点 | 基于顶点状态 |
| 收集琛申请 | 联想和交换 | 基于邻居的Value观 | 邻里 | 基于顶点状态 |

